Charting Your Course: How to Plan a Successful Database Migration to the Cloud
Migrating your database to the cloud can unlock significant benefits, including increased scalability, cost optimization, and enhanced security. However, a rushed or poorly planned migration can lead to downtime, data loss, and unexpected costs. That’s why a well-defined plan is crucial for a smooth and successful transition.
This article outlines the key steps involved in planning your database migration to the cloud, ensuring you’re well-prepared for the journey ahead.
1. Define Your Goals and Objectives:
Before diving into the technical details, start with a clear understanding of why you’re migrating. What are the specific business objectives you hope to achieve? Common goals include:
- Cost Reduction: Leverage the cloud’s pay-as-you-go model to optimize spending on infrastructure.
- Scalability and Performance: Meet fluctuating demands by scaling resources up or down as needed.
- High Availability and Disaster Recovery: Improve uptime and resilience with built-in redundancy and failover capabilities.
- Modernization: Take advantage of cloud-native database services and features.
- Improved Security: Benefit from the cloud provider’s security infrastructure and compliance certifications.
Clearly defining these objectives will guide your decisions throughout the migration process and help you measure its success.
2. Assess Your Existing Environment:
Thoroughly understand your current database landscape. This involves a comprehensive inventory and analysis of:
- Database Type and Version: Identify the database systems you’re using (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server) and their versions.
- Data Size and Structure: Determine the total data volume, table schemas, and relationships between tables.
- Workload Characteristics: Analyze your database’s performance metrics, including read/write ratios, query complexity, and peak load times.
- Dependencies: Identify applications and services that rely on the database and their connection methods.
- Security Requirements: Understand your data security and compliance needs, including encryption, access controls, and auditing.
This assessment will help you determine the optimal migration strategy and choose the right cloud database service.
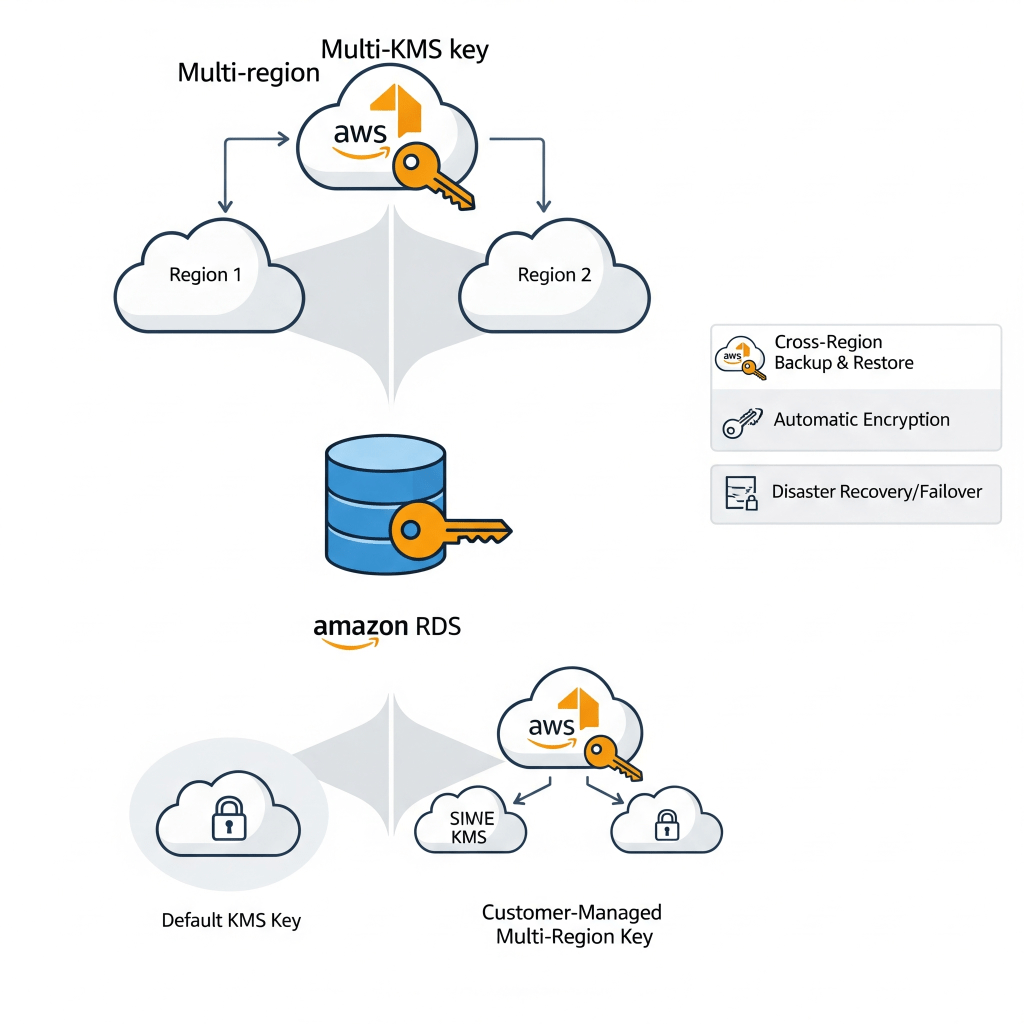
3. Choose the Right Cloud Database Service:
Selecting the appropriate cloud database service is crucial. Consider the following factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure the target database service supports your existing database type and version.
- Performance: Evaluate the performance capabilities of different options and choose one that meets your workload requirements.
- Scalability: Select a service that can easily scale up or down to accommodate your future growth.
- Cost: Compare the pricing models of different services and choose one that aligns with your budget.
- Management: Consider the level of management required. Managed database services offer simplified administration and maintenance.
- Security: Evaluate the security features of each service and ensure they meet your compliance needs.
Popular cloud database services include Amazon RDS, Azure SQL Database, Google Cloud SQL, and specialized services like Amazon Aurora and Google Cloud Spanner.
4. Select a Migration Strategy:
Several migration strategies exist, each with its own trade-offs in terms of complexity, downtime, and risk. Common approaches include:
- Rehosting (Lift and Shift): Migrating your database to a virtual machine in the cloud with minimal changes. This is the simplest option but may not fully leverage cloud benefits.
- Replatforming (Lift, Tinker, and Shift): Making small changes to your database configuration or application code to adapt to the cloud environment.
- Refactoring (Redesign): Re-architecting your database and application to take full advantage of cloud-native features and services. This requires significant effort but offers the greatest long-term benefits.
- Database Migration Service (DMS): Using a dedicated migration service to automate the data transfer process. Services like AWS DMS, Azure Database Migration Service, and Google Data Transfer Service can minimize downtime and simplify the migration.
Choose the strategy that best aligns with your goals, budget, and technical capabilities.
5. Plan for Testing and Validation:
Thorough testing is essential to ensure a successful migration. Your testing plan should include:
- Functional Testing: Verify that your applications function correctly with the migrated database.
- Performance Testing: Validate that the migrated database meets your performance requirements.
- Security Testing: Ensure that your security policies and controls are properly implemented in the cloud environment.
- Data Validation: Verify that all data has been migrated accurately and completely.
Conduct testing in a non-production environment to minimize the risk of impacting your live operations.
6. Develop a Rollback Plan:
Despite careful planning, unforeseen issues can arise during the migration. A comprehensive rollback plan is crucial to ensure you can quickly revert to your original environment if necessary. This plan should include:
- Clear Steps: Define the specific steps required to roll back the migration.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Ensure you have recent and reliable backups of your data.
- Communication Plan: Establish a communication plan to keep stakeholders informed of the rollback process.
Regularly test your rollback plan to ensure it works effectively.
7. Post-Migration Monitoring and Optimization:
After the migration is complete, it’s important to monitor the performance of your database and optimize its configuration. This includes:
- Performance Monitoring: Track key metrics like CPU utilization, memory usage, and query response times.
- Cost Optimization: Identify opportunities to reduce costs by optimizing resource allocation and storage utilization.
- Security Hardening: Implement additional security measures to protect your data in the cloud environment.
Continuous monitoring and optimization will help you maximize the benefits of your cloud database migration.
Conclusion:
Migrating your database to the cloud is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning and execution. By following these steps, you can increase your chances of a successful migration, minimizing downtime, reducing risks, and achieving your desired business outcomes. Remember to stay agile throughout the process, adapting your plan as needed based on your experiences and the evolving cloud landscape.