The Importance of Using AWS Key Management Service (KMS) Keys for Amazon RDS Databases
Introduction
Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides a wide range of services to support businesses in managing their data and applications. Among these services, Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) is a popular choice for organizations looking to set up, operate, and scale relational databases in the cloud. However, securing sensitive data stored in RDS databases is a top priority for many businesses. To address this concern, AWS offers the Key Management Service (KMS), which provides a highly secure and scalable solution for managing encryption keys. In this article, we will explore the importance of using AWS KMS keys for Amazon RDS databases and discuss best practices for implementing this solution.
Why AWS KMS Keys Are Important
AWS KMS keys play a crucial role in securing RDS data at rest and in backups. By using KMS keys, businesses can ensure that their data is encrypted both in storage and during transit, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. Additionally, KMS keys help businesses meet compliance, data security, and regulatory requirements, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Benefits of Using KMS for RDS Databases
Using KMS for RDS databases offers several benefits, including:
- Automatic encryption of storage, backups, snapshots, and replicas: KMS automatically encrypts all data stored in RDS databases, including storage, backups, snapshots, and replicas. This ensures that data is always protected, regardless of its location or format.
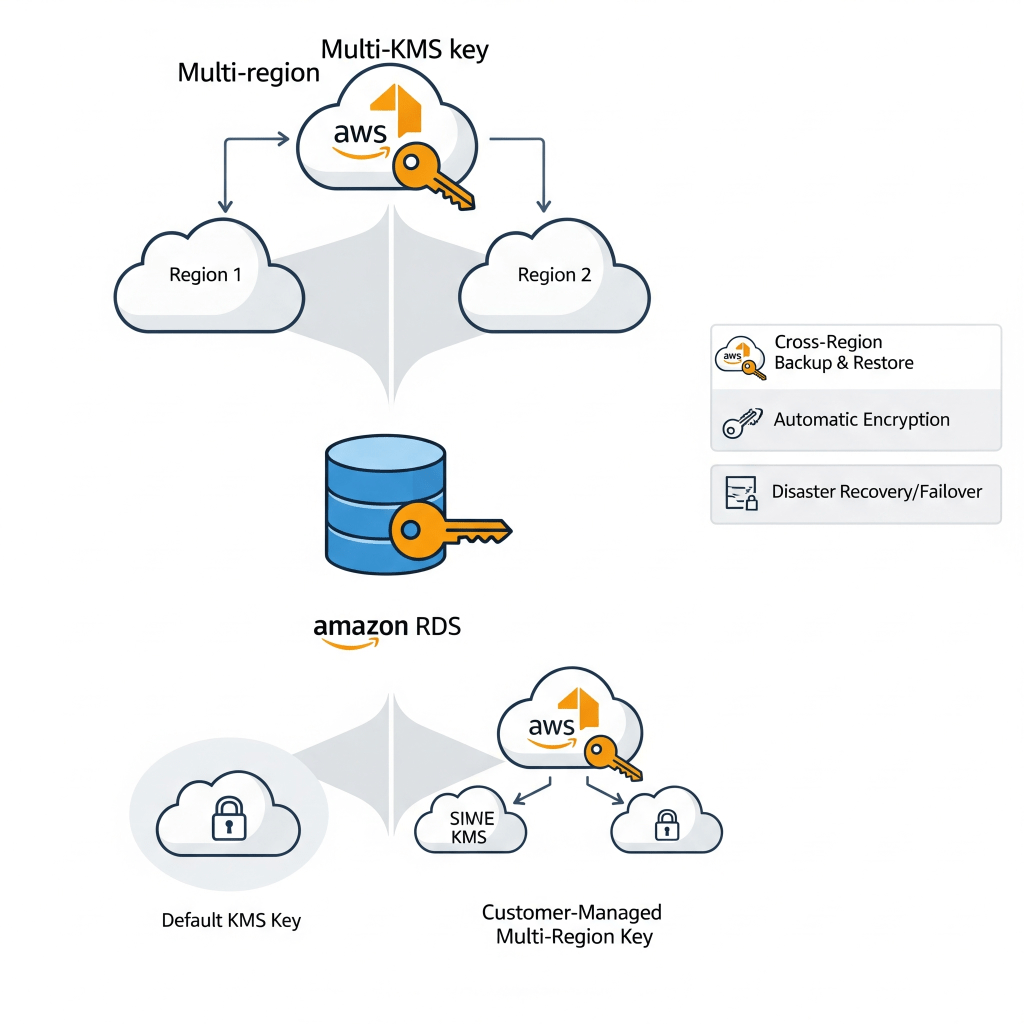
- Role in cross-region disaster recovery and security best practices: KMS keys can be used to encrypt RDS data in multiple regions, ensuring that businesses can quickly recover from a disaster or outage in one region by restoring data from another region. This approach also helps businesses meet security best practices by ensuring that data is encrypted and distributed across multiple regions.
- Why KMS Keys Should Be Multi-Region
Using multi-region KMS keys for RDS databases is essential for businesses that require cross-region failover scenarios. Multi-region KMS keys help ensure that data is encrypted and accessible in multiple regions, which can be critical in the event of a regional outage or disaster. Additionally, multi-region KMS keys can be used to perform cross-region restores and backups, providing businesses with an additional layer of data protection and redundancy.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up a KMS Key for RDS
To set up a customer-managed multi-region KMS key for RDS, follow these steps:
- Create a customer-managed multi-region KMS key: In the AWS Management Console, navigate to the KMS service and create a new customer-managed KMS key. Ensure that the key is multi-region and can be used to encrypt RDS data in all regions where your databases are located.
- Attach the KMS key to an RDS instance: Once the KMS key is created, navigate to the RDS service in the AWS Management Console and select the database instance you want to encrypt. In the Encryption section, choose the newly created KMS key as the encryption key for the database instance.
- Best practices for key rotation and IAM permissions: To ensure the security of your KMS keys, it is essential to follow best practices for key rotation and IAM permissions. Rotate your KMS keys regularly to minimize the risk of a key compromise, and ensure that only authorized users have access to the keys by managing IAM permissions effectively.
Challenges with Using the Default AWS KMS Key
While the default AWS KMS key can be used to encrypt RDS data, it has several limitations compared to customer-managed KMS keys. These limitations include:
- Limited flexibility in cross-region replication and backups: The default KMS key is region-specific, which can limit the flexibility of cross-region replication and backups. This may result in increased costs and complexity when trying to manage data across multiple regions.
- Difficulty in restoring encrypted snapshots in other regions: Restoring encrypted snapshots in other regions can be challenging when using the default KMS key, as the key may not be available in the target region. This can result in increased downtime and potential data loss in the event of a regional outage or disaster.
- Security management limitations compared to customer-managed keys: The default KMS key offers limited flexibility in managing key permissions and rotation. This can make it difficult to implement robust security policies and ensure that your data is always protected.
Conclusion and Best Practices
In conclusion, using customer-managed, multi-region KMS keys for Amazon RDS databases is essential for businesses that require a secure, scalable, and flexible solution for managing their data. By following best practices for KMS key management, businesses can ensure that their data is always protected and accessible, regardless of the location or format. Additionally, using multi-region KMS keys can help businesses meet compliance, data security, and regulatory requirements, while also providing an effective disaster recovery and backup strategy.
To summarize the key benefits of using AWS KMS keys for RDS:
- Secure and scalable encryption for RDS data at rest and in backups.
- Compliance with data security and regulatory requirements.
- Automatic encryption of storage, backups, snapshots, and replicas.
- Role in cross-region disaster recovery and security best practices.
- Multi-region KMS keys for RDS failover scenarios and cross-region restores and backups.
- Best practices for key rotation and IAM permissions management.
By implementing these best practices, businesses can ensure that their data is always protected and accessible, while also minimizing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.